Stereoisomers
Geometric isomers are molecules where the atoms are locked into their spatial arrangements via a double bond, as shown on the right. Different spatial arrangements give the molecules unique properties.
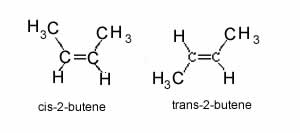
The nomenclature uses an extra prefix of either trans or cis. The two stereoisomers of 2-butene are shown on the right, you will notice that the cis isomer has the methyl groups on the same side of the double bond where as the trans isomer has the methyl groups on opposite sides of the double bond.
Alkenes that have two different substituent groups at each side of a carbon to carbon double bond can exist as stereoisomers.
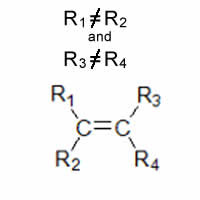
Consider the general alkene shown on the right. This alkene can exist in as cis and trans isomers only if R1 is not equal to R2 and R3 is not equal to R4.
Alkenes capable of forming cis and trans isomers. therefore, follow the general rule shown on the right.
When it comes to naming the stereoisomers the prefix cis or trans is inserted at the start of the IUPAC name.
For example 2-pentene can have two stereoisomers depending on the orientation of the alkyl groups around the double bond.
cis-2-pentene and trans-2-pentene.

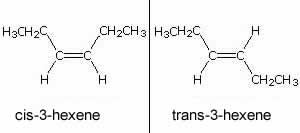
On the right is an example of the two stereoisomers of 3-hexene.
This gives us the name trans-4-ethylhept-3-ene.
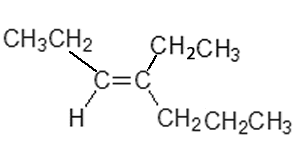
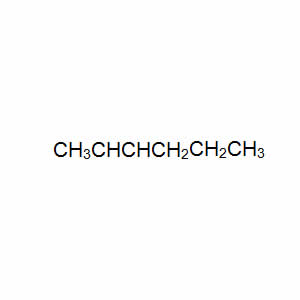
Consider the compound with the semi-structural formula shown on the right.
Draw the structural formula of each of the two possible stereoisomers and name them.
Solution
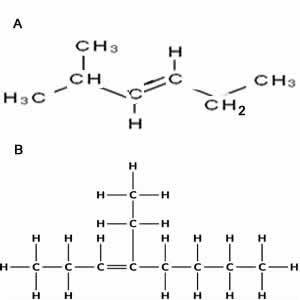
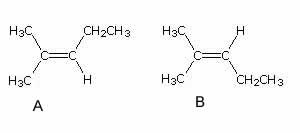
Name the molecules shown on the right.
Solution
Solution
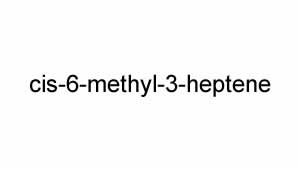
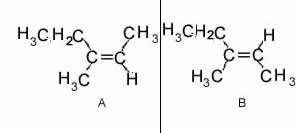
Consider the molecules shown on the right. They are
Name the molecules.
Solution
Draw the structural formula of the optical isomer with the molecular formula shown on the right. Show the chiral carbon atom.
Solution
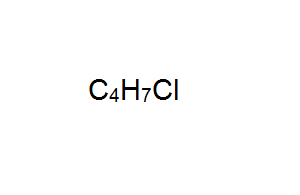
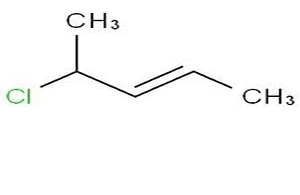
Name the stereoisomer shown on the right.
Solution
Continue with properties of cis and trans isomers.
Continue with stereoisomers in food.
Continue with optical isomers