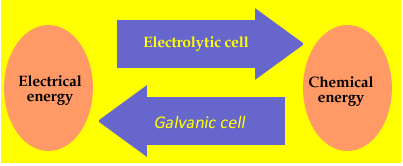
Electrolysis is derived from the Greek words meaning "splitting by electricity". An example of electrolysis is the recharging of a car battery. Recharging does not occur spontaneously and must be driven by electrical energy. This is a very important difference between galvanic and electrolytic cells. Reactions taking part during the discharge of a galvanic cell are spontaneous, where as those taking part in an electrolytic cell must be driven by the supply of energy. The difference can be summarized in the diagram on the right.
Similarities and differences between electrochemical and electrolytic cells are listed in the table below.
|
Electrochemical
(galvanic)
|
Electrolytic
|
|
|
Oxidation
|
Occurs
at the anode
|
Occurs
at the anode
|
|
Reduction
|
Occurs
at the cathode
|
Occurs
at the cathode
|
|
Polarity
of the anode
|
Negative
|
Positive
|
|
Polarity
of the cathode
|
Positive
|
Negative
|
|
Energy
|
Produced
|
Supplied
|
|
Electron
flow
|
From
-ve to +ve
|
From
+ve to -ve
|
| Salt bridge | Required | Not required |
| Direction of electron flow | Anode=>Cathode | Anode=>Cathode |
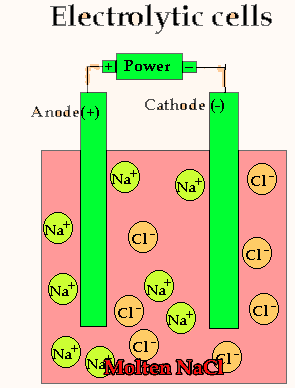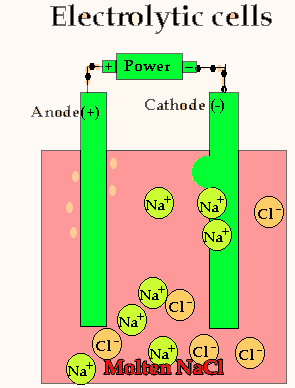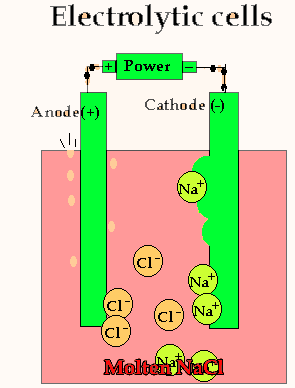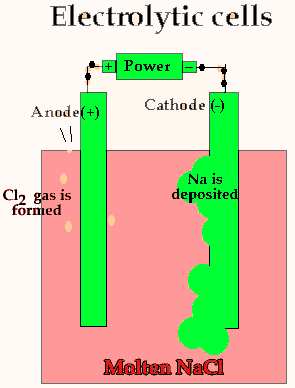
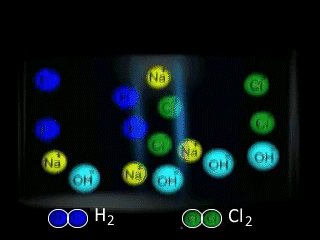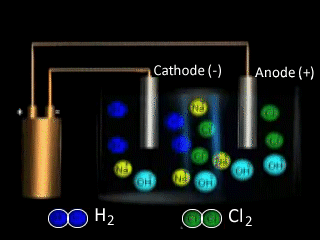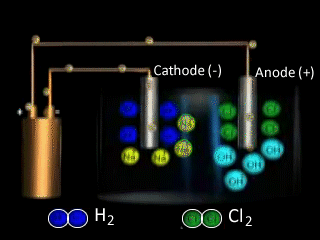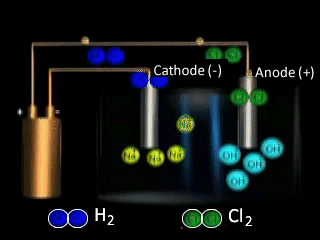
Lets take the decomposition of molten NaCl(pictured above) as our first example, as this is a relatively simple electrolytic process since only one reaction is possible at each electrode. The power source simply acts as an electron pump pulling electrons out of the anode and pumping them into the cathode.
The chloride ions are now attracted
to the positive electrode (anode) and undergo oxidation.
In an electrolytic cell the strongest oxidant and strongest reductant will react.
The strongest reductant will be oxidised at the (+) anode and the strongest oxidant will be reduced at the (-) cathode. Only when these have expired will the next strongest species, according to the electrochemical series react.
So when predicting the products that will form at each electrode follow the two steps below
.
Step 1 Using the electrochemical series identify the strongest oxidant that makes contact with the cathode(-) or is the cathode(-).
Step 2 Using the electrochemical series identify the strongest reductant that makes contact with the anode(+) or is the anode(+).
Why is NaCl electrolysed in the molten form to produce sodium metal as opposed to the aqueous form? The video on the right shows the electrolysis of a brine solution which is another word for concentrated NaCl solution.
What reaction is occurring on the anode?
What reaction is occurring at the cathode?
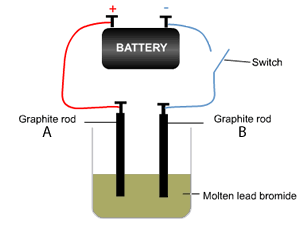
The decomposition of molten lead bromide takes place using the apparatus shown on the right, where a current is passed through the electrodes. The reaction proceeds when the switch is closed. Using a table of the electrochemical series answer the following questions.
a) Which electrode is the anode?
b) Which electrode is the cathode?
c) What type of reaction takes place at the anode and the cathode?
d) Write the equation of the reaction taking place at the cathode and the anode. Solution
e) Which electrode would increase in mass? Explain
f) Would a solution of PbBr2 produce the same products? Explain using the table of half cell potential.
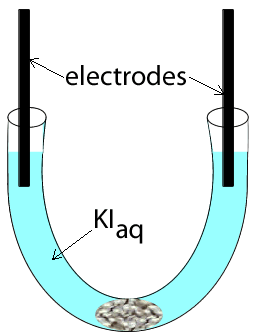
Potassium iodide was placed in a u-tube and electrodes, attached to a power source, were inserted at each end. A cotton wool plug was inserted at the bottom of the u-tube, as shown on the left.
The power supply was then turned on and charge was allowed to flow for several seconds. View the video on the left and answer the questions below.
1) What are the possible reactants present?
2) A brown substance is seen to form on the electrode on the left
a)
Identify the substance formed
b) Write an equation for the reaction that is occurring at this electrode
c) This electrode is the
3) A gas is seen forming on the electrode on the right. A red litmus is inserted into the solution surrounding the electrode and it quickly turns blue.
a) Identify the gas formed
b) Write the equation for the reaction occurring at this electrode.
c)
This electrode is the
4) Name the oxidant and reductant taking part in the half reactions?
5) Write the equation for the overall reaction.
Click for the audio of the solution