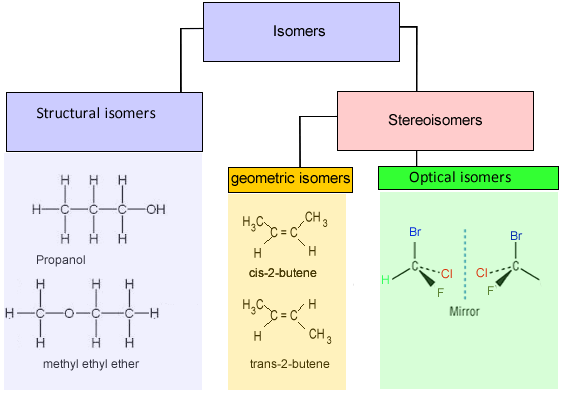
| There are two types of isomers, structural isomers and stereoisomers. Structural isomers or, as they are sometimes called, constitutional isomers, are
compounds that have the same chemical formula but a different structural
formula. These molecules are bonded together in totally different ways.
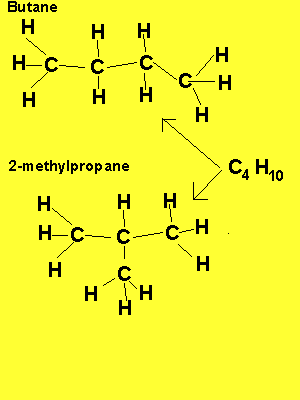
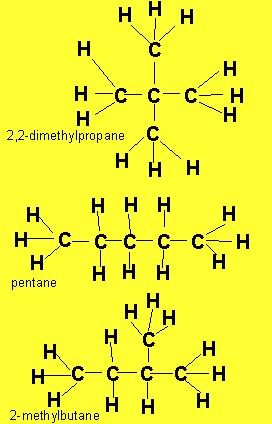
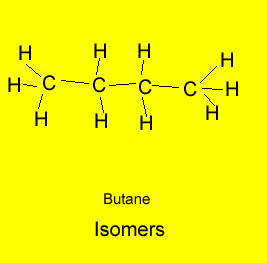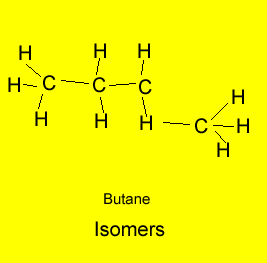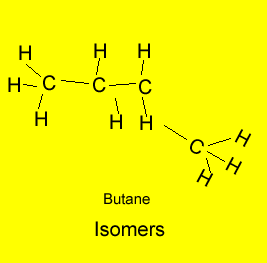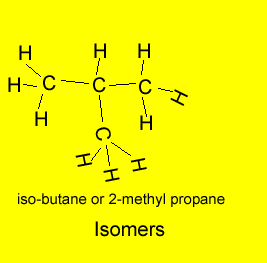
The example above shows propanol and methyl ethyl ether both of which have the same molecular formula of C3H8O but as shown above totally different structural formulae. Take, also, butane, it has the molecular formula C4H10, however, 2-methylpropane also has the molecular formula C4H10. Butane and 2-methylpropane are examples of structural or constitutional isomers.
|