Energy changes during chemical reactions
Exothermic reactions (-ΔH)
Chemical energy is the sum of two types of energies, kinetic energy and potential energy and is given the name enthalpy (H). Kinetic energy comes from the movement of molecules in the gas and liquid phase or the vibration of particles in a solid. Potential energy is stored energy and results from such interactions as:
- repulsion between nuclei;
- attraction of nuclei and electrons;
- bond vibration and rotation;
- electron repulsion.
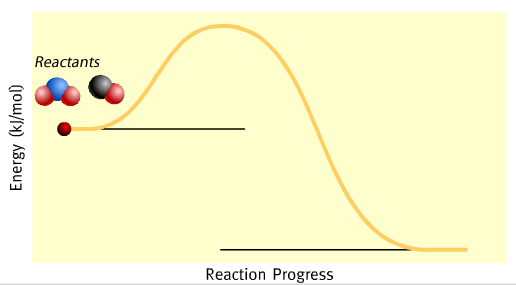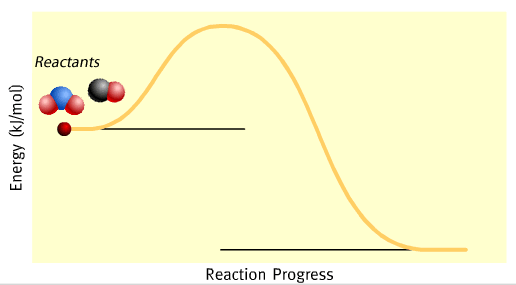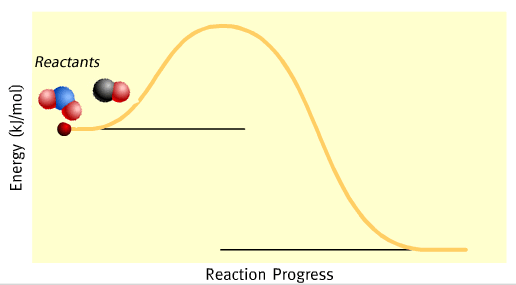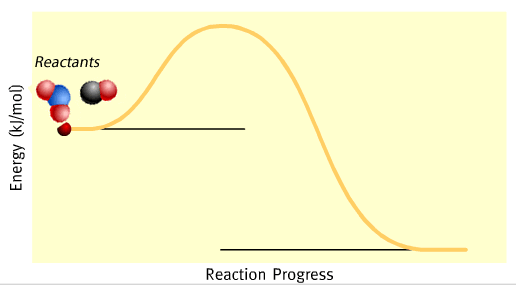
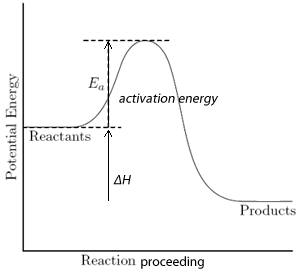
We can show energy changes during a chemical reaction using energy profiles. The energy profile of the reaction between nitrogen dioxide and carbon monoxide is shown on the left while the equation is given below.
NO2(g) + CO(g) => CO2(g) + NO(g) ΔH= –226 kJ mol–1
The symbol ΔH is the difference between H(products) - H (reactants)The negative sign indicates that energy is given out.
As you can see from the energy profile, the chemical energy of the reactants is greater than the products. The difference in energy is given out, during the reaction, as heat.
Initially, when mixed together, the reactants lack sufficient energy to react. Their collisions are not strong enough to initiate a reaction by breaking bonds.
After a small amount of energy is supplied, known as activation energy, the reaction proceeds. In this case the activation energy for this reaction is shown on the energy profile as 132 kJ mol–1. An activated complex forms which then splits to form the products.
At completion of the reaction 226 kJ of energy is given out for every mol of NO2 that reacts.
Click to see the Flash animation(source Youtube)
.Another example of an exothermic
reaction is the combustion of methane in oxygen. The equation for the reaction is shown below.
CH4
(g) + 2O2(g) => CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) ΔH = -890 kJ mol–1
The negative ΔH indicates that the energy content of the products is less than the energy content of the reactants. Like many other reactions methane will not spontaneously react when mixed with oxygen. Energy has to be supplied, activation energy to start the reaction.
Click the video on the right. It shows the reaction between methane and oxygen and its energy profile.
Activation energy forms bonds
No collisions occur between methane and oxygen prior to adding activation energy.
When a spark or flame is added to the methane-oxygen mixture collisions between molecules occur to produce an activation complex.
Exothermic reactions release heat and have a negative ΔH.
A negative ΔH indicates that the products have more energy than the reactants.
Bond breaking requires the input of energy while bond formation releases energy.
Continue with thermochemical equations