Homeostasis is the maintenance of a constant internal environment of a cell or an organism, despite fluctuations in the external environment. It has evolved because it gives some organisms a survival advantage. Maintaining a constant body temperature, where enzyme activity is at its optimum level, enables animals to hunt even in freezing conditions. Homeostasis is therefore energy consuming. Some animals prefer not to waste energy maintaining body systems constantly at the ready and reduce their level of activity during cold months by hibernating, such as bears, or remaining dormant as in the case of insects. Homeostasis works by way of feedback mechanisms. Examples include the maintenance of the blood at a specific pH range and body temperature. Systems such as the urinary and respiratory systems work in isolation or in concert to maintain homeostasis.
Feedback mechanisms involve:
- Receptors in the body that pick up specific changes. this may include heat or blood glucose levels.
-
A control centre, in most cases it is the brain, that regulates the response.
- Effectors, muscles or organs, that are stimulated to cause an effect that corrects the deviation in the internal conditions.
The effectors are stimulated until the response has returned the body back to a state of balance and the receptors are no longer active.
Two types of feedback mechanisms exist, negative and positive feedback.
Negative feedback acts in such a way as to reverse the change that has occurred, while a positive feedback acts to enhance the change that has taken place. In fact most of the life sustaining processes in our body operate on negative feedback.
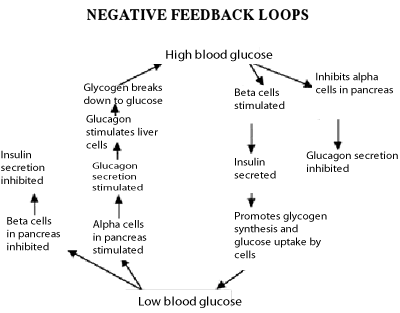
Insulin is a hormone,like all hormones, it is a chemical secreted into the blood by an endocrine organ and carried around the body to a target organ. Insulin helps to control the amount of glucose dissolved in the blood. It prevents the blood sugar level from rising too high by initiating pathways for glucose to enter the cells. Without insulin cells can only get energy from fat and this causes serious problems. The control of blood sugar level is a homeostatic mechanism. |
The Explanation
-
Insulin is secreted by the Islets of Langerhan which are special groups of cells in the pancreas.
- After a carbohydrate meal, the level of glucose in the blood will start to rise as the digestive system breaks up and absorbs carbohydrates as glucose.
- After several hours without a meal, the blood sugar level will fall as cells use up the glucose in aerobic respiration.
- As the blood sugar concentration rises, the Islets of Langerhan are stimulated to secrete insulin.
- Although most cells in the body respond to insulin the main target organ for insulin is the liver. It is there that glucose is converted into glycogen. Excessive intake of carbohydrates saturates glycogen stores in the body and causes excess glucose to be stored as fat.
- When blood sugar levels fall, not only does the pancreas make less insulin, but it is stimulated to produce another hormone called glucagon. Glucagon acts on the liver to cause the breakdown of glycogen into glucose before releasing it into the blood. Glucagon has the opposite effect of insulin.
- Negative feedback causes the release of insulin and glucagon to slow down when blood sugar levels drop to normal levels.
An example of a positive feedback mechanism is that of child birth. Receptors in the uterus detect the pressure of the unborn child's head. The signal is transmitted to the pituitary gland where it responds by releasing oxytocin. Oxytocin causes the uterus to contract causing the head to put more pressure on the uterus and causing receptors to continue firing thus causing further secretion of oxytocin. This causes the uterus to continue to contract until the baby is born.

The temperature control mechanism of the hypothalamus can also be complex.
View the video on the right.
In homeostatic temperature control of the skin identify the:
- receptors;
- control centre;
- effector.
In homeostatic temperature control of the blood identify the:
- receptors;
- control centre;
- and a number of effectors
Frost bite is a condition where by the skin is allowed to cool to the point where cells freeze and die. What balance is the body trying to achieve by allowing the skin to freeze?
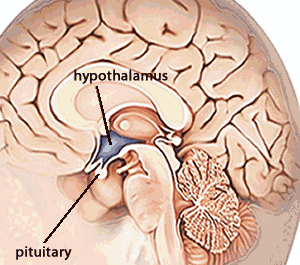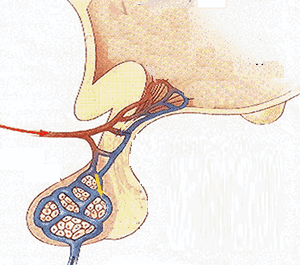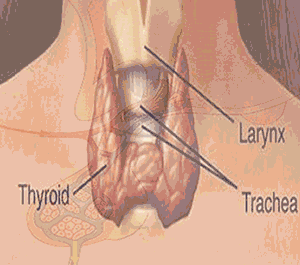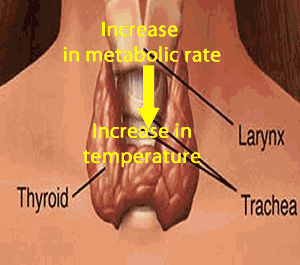
What is the role of the hormone thyroxin in controlling core body temperature?
Homeostatic sensors are structures .
A specialised protein molecule on the surface of a cell's membrane can be termed a
A structure that is responsible for processing and interpreting information received by sensory cells is known as a
Elements that respond to the controllers and have the function of bringing about actions that regulate and maintain the equilibrium of the organism are known as
Which of the following are not effectors?
Homeostasis is maintained primarily via feedback mechanisms.
Which of the following is an example of a positive feedback loop?
A) A neuron is stimulated, thus opening membrane channels to allow sodium ions to leak from the extracellular fluid to the intracellular fluid. This causes more membrane channels to open, thus allowing more sodium ions to enter the intracellular fluid.
B) Baroreceptors notify the brain that the blood pressure has increased. The brain then notifies the blood vessels to dilate, thus lowering the blood pressure.
C) Low levels of glucose in the blood cause the pancreas to release less insulin (a hormone that lowers blood glucose).
D) Elevated body temperature is sensed by cells in the brain. As a result, sweat is produced, and heat is lost as the water in the sweat evaporates.
E) An auto factory produces 1000 cars per week. The sales office could sell 1200 cars per week. Extra production personnel are added at the factory to meet the sales demand.
If a response enhances an original stimulus, the system is classified as a
Define the term homeostasis and identify the components of a typical feedback loop. Explain the role of each component.
Why do insects remain dormant during the cold months of winter?
Birds and mammals are homeotherms, that is, their body temperature never fluctuates beyond a narrow range. What does this mean about their level of activity in different climates? What is the draw back of maintaining a constant body temperature?
Fish are considered to be poikilotherms. Poikilotherms have very little behavioural adaptations to maintain body tempearture and are at the mercy of the environment. Fish have many different enzymes that function at different temperatures. How does this benefit the fish?
Ectotherms, such as lizards, never achieve constant body temperature. They rely on many behavioural adaptations to increase their body temperature and hence increase their level of activity. Reptiles seek shade in hot conditions and rest in direct sunlight when it is cold. Fish and reptiles must create the right internal body conditions for enzymes to function properly. How do fish and reptiles differ in maitnining ideal conditions for optimal enzyme activity.?
Insects are only active during the Summer months. Insects are
What are some advantages for insects being active only in summer?
Consider the animation on the right. It shows the response to hypothermia of the Human body. After viewing the video above answer thte questions below?
1) What glands are involved in this response?
2) What ultimately are the effectors?
3) How many control centres are in involved? Name them and describe what the stimulus and response is for each.
4) What is the stimulus for the release of:
- TSH
- Thyroxin
- Releasing hormone
5) What is the response to each of the hormones above?
6) What is the effect?