Negative feedback loops act to undo the changes induced by a stimulus. Negative feedback loops are essential for maintaining homeostasis in complex organisms.
An example of a negative feedback loop involved in homeostasis is the maintenance of blood pressure in the human body. Special pressure receptors in the heart and aorta detect fluctuations in blood pressure. Nerves carry this information to the brainstem (medulla oblongata). When blood pressure drops, the brainstem sends a signal , via nerves, to the heart to increase the rate of beating and to the blood vessels to constrict. This increases blood pressure throughout the body.
On the other hand, if the blood pressure is high, the brainstem sends signals to the heart to slow down and to the blood vessels to dilate, thus lowering blood pressure.
Maintaining blood pressure is critical as damage to internal organs can occur due to high pressure or loss of consciousness due to low pressure.
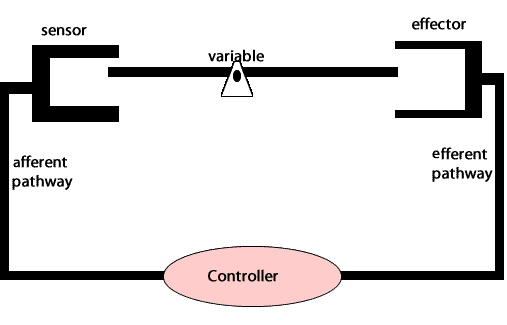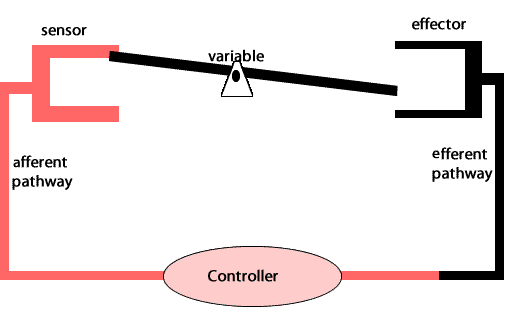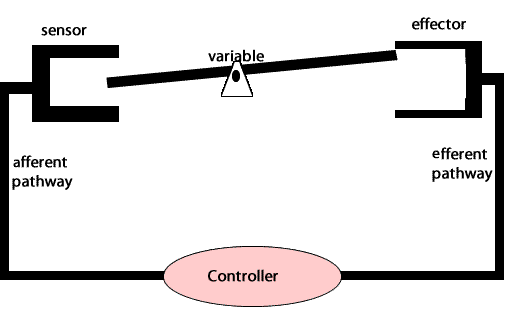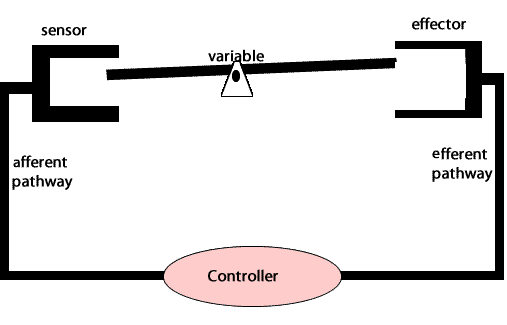
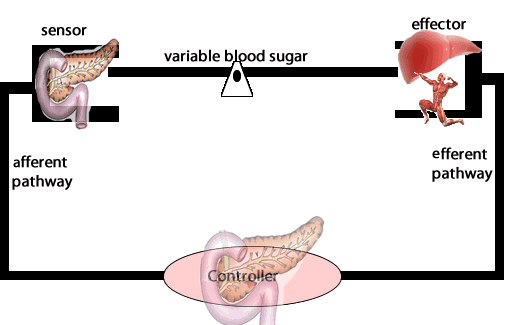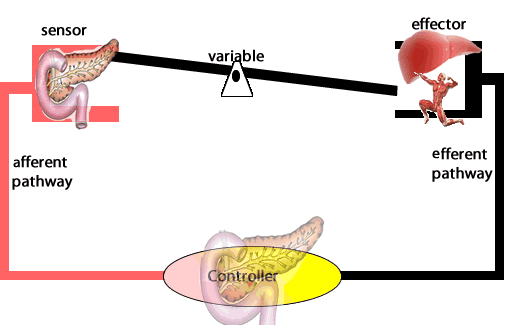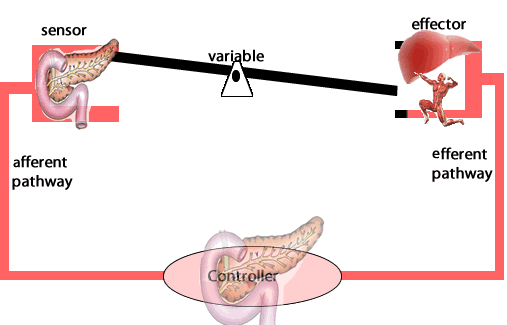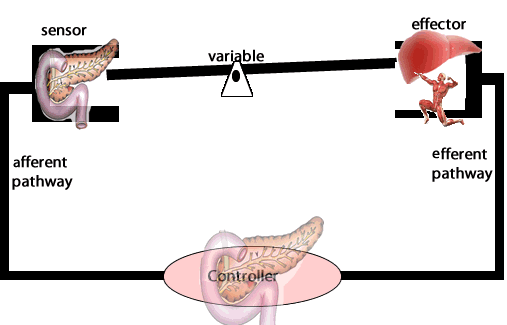
Another example of negative feedback during homeostasis is the regulation of blood sugar levels. The right amount of glucose in the blood is between 0.9 and 1.1 grams/litre. Higher levels of sugar in the blood damage them. The amount of glucose in the blood is sensed by variety of cells. If the amount of glucose is too high, beta cells in the pancreas act as receptor and controller releasing the hormone insulin. Insulin stimulates muscle cells of the body to take up glucose and the liver cells to store glucose as glycogen.
1) Explain why some describe homeostasis as a dynamic equilibrium?
2) a) In the control of high blood pressure, describe the:
receptor,
control center,
effector,
response.
b) In the control of hyperglycemia, describe the:
receptor,
control center,
effector,
response.
3. How does a negative feedback loop alter the initial change in the variable?
4) What are the three primary structures needed for homeostasis?
5) A part of the brain that monitors the value of a certain condition and acts to restore its right value is known as the
6) A sensory organ that gathers information about the environment is known as the
7) Shivering is a muscular response to cold. Muscles contract in order to create heat. Muscles are known as
8) In the control of blood pressure what is the control centre or integrator?
9) In thermoregulation, the temperature of the blood is monitored by the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus will stimulate the vasodilation or vasoconstriction, shivering or sweating depending on the temperature of the blood.
a) Sweat glands are known as
b) The hypothalamus is the