1) Consider the following reaction.
![]()
Which reaction conditions would give the greatest yield of nitrogen dioxide, NO2?
A. 200 kPa and 100 °C
8. 200 kPa and 25 °C
C. 100kPaand100°C
D. 100 kPa and 25 °C
Solution
2) An example of a homogeneous equilibrium is the decomposition of sulfur trioxide, SO3(g), to form sulfur dioxide, SO2(g), and
oxygen, O2(g).
Some SO3(g) is placed in an empty container, which is then sealed.
Which one of the following statements is true at all temperatures when the sealed system reaches equilibrium?
A. The mass of SO2(g) is 4.0 times the mass of O2(g).
8. The mass of SO2(g) is 80.0% of the mass of SO3(g).
C. The amount in mol of SO2(g), and O2(g) are the same.
D. The amount in mol of SO2(g), and SO3(g) are the same.
Solution

3) The reaction between iron(III) ions, Fe3+(aq), and thiocyanate ions, SCN- (aq), produces iron(III) thiocyanate ions, FeSCN2+(aq).
![]()
A few drops of sodium thiocyanate solution, NaSCN(aq), are added to 200 ml of the equilibrium mixture at constant temperature.
The concentration-time graph shows the change in concentration of SCN-(aq).
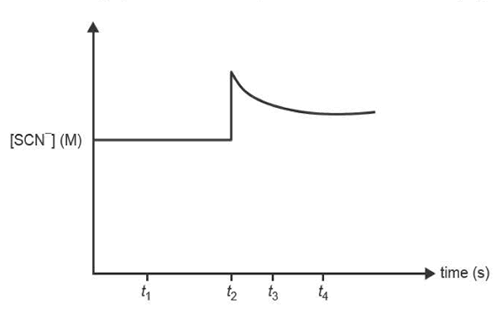
Which one of the following statements is true?
A. The equilibrium constant at t4 is lower than at t1 .
B. The chemical energy of the system increases between t3 and t4 .
C. The rate of the reverse reaction is less than the rate of the forward reaction at t3 .
D. Both the concentrations of Fe3+ and FeSCN2+ are higher at t3 than at t1.
Solution

4) Ammonia gas, NH3(g), can be made by reacting a mixture of nitrogen gas, N2(g), and hydrogen gas, H3(g), using an iron catalyst.
The reaction can be represented by the equation
![]()
The equilibrium constant, KP, at 400 °C is 1.60 x 10-8 kPa-2.
In a mixture that is at equilibrium at 400 °C, the partial pressure of H2 is 88.7 kPa and the partial pressure of N2 is 43.4 kPa.
a. Write the expression for the equilibrium constant, Kp. 1 mark
Solution
b. Determine the partial pressure of NH3 , in kPa, in the equilibrium mixture at 400 °C. 1 mark
Solution
c. At a constant temperature of 400 °C, a change was made to the equilibrium system. Just after the change was made, the reaction quotient, Q, was 1.20 x 10-9 kPa-2.
Identify a change to the system that would result in this reaction quotient. Explain how the system would respond to the change.
2 marks
Solution

d. Explain how the iron catalyst addresses the conflict between optimal rate and temperature considerations in the production of NH3 Support your answer with reference to one green chemistry principle. Refer to item 26.ii of the Data Book. 3 marks
Solution
