Science as a human endeavour- Understanding our Solar System
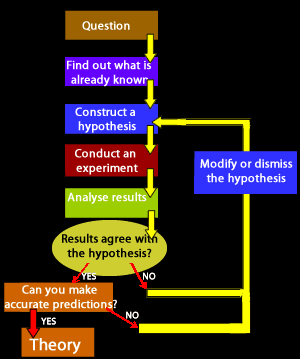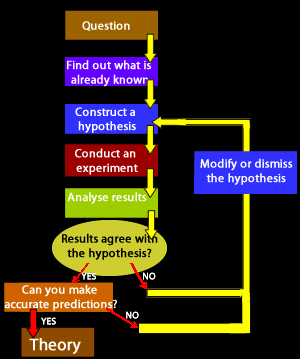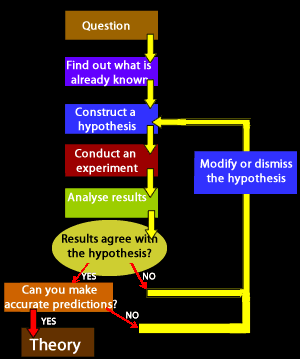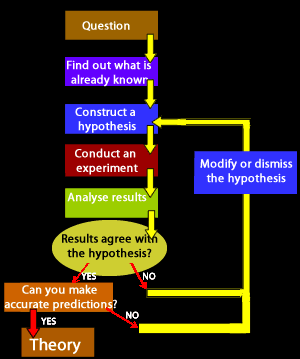
The Scientific Method is a set of procedures designed to obtain reliable knowledge from the world around us. Procedures consists of systematic observation, measurements and experimentation which ultimately lead to the formulation of a hypothesis, its testing and modification or acceptance.
Only when the hypotheses has overcome rigorous testing, as outlined in the diagram on the right, is it excepted as a theory.
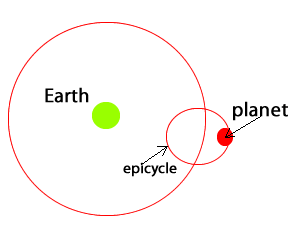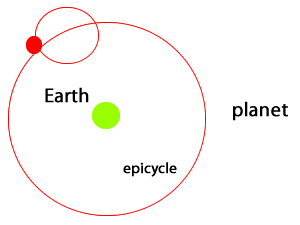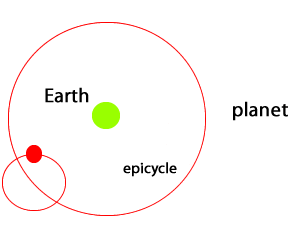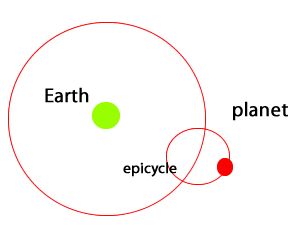
Ptolemy took Aristotle's incorrect theory one step further by combining his observations of the movement of the stars with geometry. In doing so, he was able to predict the movement of planets in the night sky. The geocentric model was not only able to explain observations of planetary motion but also predict them. However, in order for the model to predict accurately planetary motion it required that planets orbit in smaller circles called epicycles as they moved around Earth. This flawed view of the Universe was accepted for many centuries until technology, in the form of a telescope, was able to shed more light on our understanding of the Solar System.
During this unit of work students will be exposed to the scientific thinking involved throughout the ages to establish a model of the Solar System based on observation and prediction demonstrating the use of the Scienctific Method.
Student should be able to:
- Outline the sequence of steps of the Scientific Method.
- Outline the differences between the geocentric and heliocentric models for the solar system.
- Outline the work of scientist that eventually lead to the acceptance of the heliocentric model.
- Discuss the technological breakthrough made by Galileo and the observation that resulted in a bias to the heliocentric model of the Solar System.
- Discuss Kepler's contribution to the developme.nt of a model to describe the Solar System.
- Describe how Copernicus revolutinised scientific thinking during his time.
Continue with the difference between a hypothesis, a scientific law and a scientific theory