1) Cold weather can affect the performance of diesel fuels, such as petrodiesel and biodiesel. As the temperature is lowered, a point is reached at which the larger molecules in the fuel begin to solidify out of the liquid. When this point is reached, the fuel starts to become cloudy. The temperature at which this point is reached is known as the cloud point. Which statement is correct?
A. A high cloud point indicates that the diesel fuel is a biodiesel and will produce more pollutants.
B. A low cloud point indicates that the diesel fuel is a biodiesel and has good hygroscopic properties.
C. A low cloud point indicates that the diesel fuel is a petrodiesel and will flow readily in cold temperatures.
D. A high cloud point indicates that the diesel fuel is a petrodiesel and contains only straight-chain carbon molecules.
Solution

2) A car is powered by the combustion of a fuel in the engine and, historically, the fuel has been petrol. Ethanol, C2H5OH, and hydrogen, H2, are now being used as alternative fuels in cars. A significant component of petrol is 2,2,4-trimethylpentane, C8H18, which has the same molar heat of combustion as octane, C8H18.
i. Write the balanced thermochemical equation for the combustion of
C8H18 in excess oxygen, O2.
ii. Calculate the mass of carbon dioxide, CO2, in kilograms, released during the complete combustion of 1.00 kg of C8H18.
M(C8H18) = 114 g mol–1
Solution

iii. An alternative means of providing power to cars is the combustion of H2 in fuel cells. If 582 L of H2 (measured at 100 kPa and 18 °C) were combusted, what amount of energy, in megajoules, would be released?
Solution

iv. H2 can be produced by several methods. Two of these methods are given below.
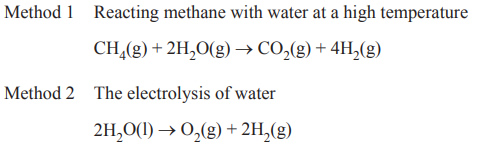
Evaluate the environmental impacts of each of these methods of producing H2.
Solution
