1) Thymine makes up 27% of the number of bases in a double strand of wheat DNA.
Wheat DNA also contains
A. 23% adenine.
B. 23% cytosine.
C. 27% guanine.
D. 46% guanine.
Solution

2) Maltotriose is a trisaccharide that is formed when three glucose molecules link together. The molar mass of glucose, C6H12O6, is
180 g mol–1.
The molar mass of maltotriose is
A. 472 g mol–1
B. 486 g mol–1
C. 504 g mol–1
D. 540 g mol–1
Solution

3) Amino acids can be classifi ed according to the nature of their side chains (Z groups). These may be polar, non-polar, acidic or basic.
Referring to the data book, name one amino acid that has a non-polar side chain and one amino acid
that has an acidic side chain.
Solution

4) The table below provides examples of different categories of side chains at a pH of 7.
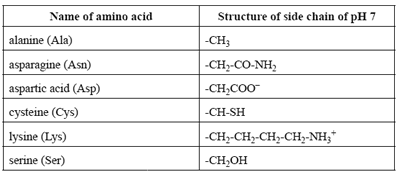
The tertiary structure of proteins is a result of the bonding interactions between side chains of amino acid residues.
Use the information provided in the table above to
i. identify the amino acid that is involved in the formation of disulfide bonds (sulfur bridges)
Solution

ii. give an example of two amino acid side chains that may form hydrogen bonds between each other
Solution

iii. give an example of amino acid side chains that may form ionic bonds (salt bridges) between each other
Solution

iv. identify the type of bonding that exists between the side chains of two alanine residues.
Solution

5) The enzyme trypsin catalyses the breaking of peptide bonds in proteins. Trypsin is active in the upper part of the small intestine, where the pH is between 7.5 and 8.5.
Trypsin is not effective in the stomach, where the pH is 4.
Suggest a reason why.
Solution
