1) Hydrogen gas is an energy source. Researchers are investigating the production of hydrogen gas in a microbial
electrolysis cell.
The cell is made up of an anode half-cell and a cathode half-cell. The half-cells are separated by a proton exchange membrane, as shown in the diagram below.
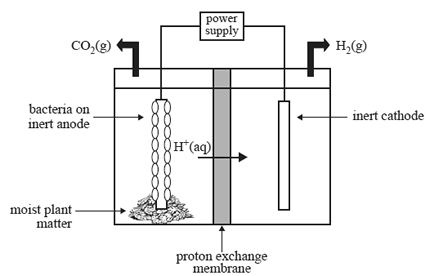
A number of reactions take place in the cell, resulting in the production of hydrogen. These reactions are summarised
below.
Anode half-cell
• The anode half-cell contains moist plant matter and electrochemically active bacteria that live on an inert anode.
• The gaseous mixture that is present in the half-cell does not contain oxygen.
• The moist plant matter ferments to produce ethanoic acid (CH3COOH). Bacteria on the anode consume the
ethanoic acid and release hydrogen ions, electrons and carbon dioxide gas. A small voltage is then applied to
reduce the H+ ions.
Cathode half-cell
• The cathode half-cell contains an inert cathode.
• The gaseous mixture that is present in the half-cell does not contain oxygen.
• The released hydrogen ions and electrons react to form hydrogen gas, as shown in the equation below.
2H+(aq) + 2e– => H2(g)
a. Ethanoic acid is converted to carbon dioxide gas and H+ ions at the anode.
Write an equation for this reaction.
Solution

b. On the diagram above, use one arrow to indicate the direction of electron flow in the cell when an external voltage is supplied to the cell by the power supply.
Solution

c. Hydrogen gas is not produced at the cathode if oxygen is present in the half-cell.
Write a balanced half-equation to show the product that would be produced at the cathode if oxygen were present in the half-cell.
Solution

d. Describe one difference between an electrolysis cell and a traditional fuel cell.
Solution

2) A teacher demonstrated the process of electrolysis of a molten salt using an unknown metal salt, XBr2.
The apparatus was set up as shown below.
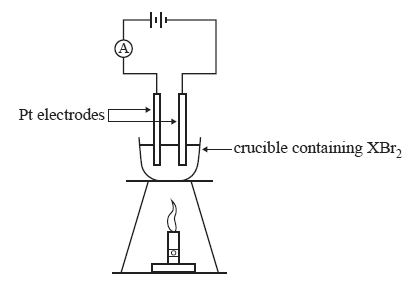
At the conclusion of the demonstration, the students were provided with the following information.
• A current of 1.50 amperes was applied for 30.0 minutes.
• 2.90 g of metal X was produced.
a. Write a balanced half-equation for the anode reaction in this electrolytic cell.
Solution

b. Determine the amount, in mol, of metal X that was deposited on the cathode.
Solution

c. Identify metal X.
Solution