1) Which of the following represents a balanced reduction half-reaction?
A. VO2++ H+ + 2e– → VO2+ + H2O
B. VO2++ H2 → VO2+ + H2O + e–
C. VO2++ 2H+ + e– → VO2+ + H2O
D. VO2++ 4H+ + 3e– → VO2+ + 2H2O

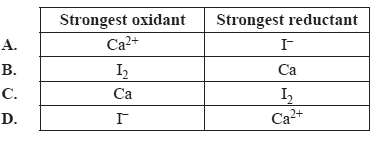
2) Identify the strongest oxidant and the strongest reductant in the following half-equations.
Ca2+(aq) + 2e– =>Ca(s)
I2(s) + 2e– => 2I–(aq)
Solution
3) A direct electric current is passed through 1.0 M K2SO4 solution using inert electrodes. The following standard reduction
potential is provided in addition to those in the Data Book.
S2O82–(aq) + 2e– => 2SO42–(aq) E0 = 2.01 V
Which one of the following equations represents the reaction that occurs at the anode?
A. 2SO42–(aq) => S2O82–(aq) + 2e–
B. 2H2O(l) => O2(g) + 4H+ + 4e–
C. 2H2O(l) + 2e– => H2(g) + 2OH–(aq)
D. K+(aq) + e– => K(s)
Solution

4) Which one of the following statements is true for both fuel cells and rechargeable cells?
A. All reactants are stored within the cell.
B. Reaction products are continuously removed from the cell.
C. Electrons pass from the reductant to the anode as electricity is produced.
D. Electrical energy is converted to chemical energy as the cell is recharged.
Solution
5) Why is it not possible to plate an object with magnesium metal using an aqueous 1.0 M MgI2 solution as the electrolyte?
A. Water is a stronger reductant than I–
B. Water is a stronger oxidant than I–
C. Water is a stronger reductant than Mg2+
D. Water is a stronger oxidant than Mg2+
Solution
