Tea Cake and Chemistry

Ingredients and utensils.
Sieve
4 X eggs
300g Plain Flour
300g Apricot jam or any other jam of choice
Teaspoon of Baking Soda
75mL of sunflower oil
1/4 cup of sultanas or any other dried fruit of choice.
Oil spray to grease the baking tin with.
Glass cup.
Glass mixing bowl.
22cm round baking tin
Whisk
Step 1 Place 300g of jam into a large glass bowl with one teaspoon of baking soda. Use a whisk to stir the mixture completely into a uniform consistency.
Step 2 Once the baking soda and jam have been throughly mixed add four eggs and 75 mL of sunflower oil and again use a whisk to thoroughly mix the eggs and oil into the jam and baking soda mixture.
Step 3 Use a sieve to slowly add 300g of plain flour to the mixture while stirring.
Step 4 Now add 1/4 cup of dried fruit of your choice and once again stir the mixture well.
Step 5 Prepare a baking tin by spraying lightly with oil and then using a tissue paper to spread the oil so that it covers the entire internal surface of the baking tin.
Step 6 Place the glass cup upside down in the middle of the tin and pour the mixture in.
Step 7 Bake for 25-30 minutes in a preheated oven at 180oC .


When NaHCO3 is heated it decomposes into carbon dioxide gas, water and a harmless substance known as sodium carbonate Na2CO3.
As for the fluffy, soft texture of the cake, well, that's due to a gas formed inside the dough mixture as it is heated in the oven. Not only does heat encourage the chemical reaction that forms this gas, but once formed, heat also causes the gas particles to form bubbles of gas in the dough mixture that expand to produce countless little air pockets that make the cake rise and increase in volume. Cakes are usually soft because of this reason.

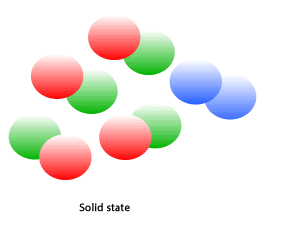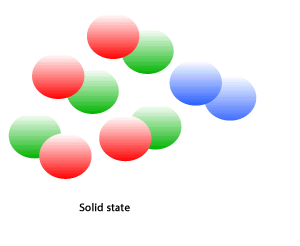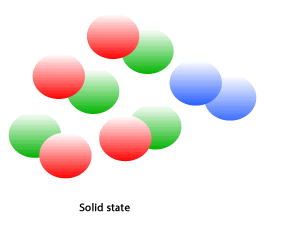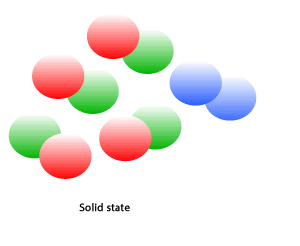
The formation of carbon dioxide is an example of a chemical change. A chemical reaction often results in:
- a colour change
- the irreversible formation of a solid, liquid or gas. Bubbles in solution or an odor can indicate the presence of a gas.
Chemical reactions take place during cooking. A chemical reaction takes place when particles can mix together and collide with enough force to break apart and rejoin in different combinations to form new substances. The animation on the right shows how.
1. Use knowledge of particle theory to explain:
- why is heating necessary in order to cook.
- what happens to particles in the solid state when heated
- what happens to particles in the liquid state when heated
- what happens to particles in the gas state when heated.