Ocean sequestration of CO2
The oceans currently have an annual uptake of carbon dioxide of 2 Gt directly from the atmosphere.
Direct injection of carbon dioxide into the deep ocean water is proposed as a means of trapping and sequestering carbon dioxide.
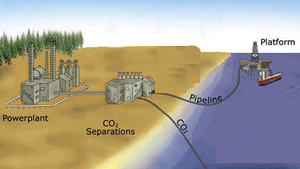
The deep ocean layers are highly unsaturated in carbon dioxide when compared to the solubility of carbon dioxide at temperatures around -2°C and pressures of 100 atm that exist at these depths
If all man made carbon dioxide entered the oceans every year it would increase the total ocean concentration of carbon dioxide by 0.016% per year.
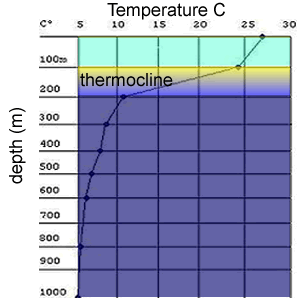
So it is hoped that ocean sequestration of carbon dioxide can provide a solution to reducing the CO2 emissions. At such high pressures of 100 atm and low temperatures of -2 oC carbon dioxide can be safely stored in relatively stable bodies of water.
Since no formal, large scale investigations have been so far undertaken it is difficult to predict the impact of large scale capture and ocean sequestration of carbon dioxide. Impact of carbon dioxide on pH of waters and local sea environments, just to name a couple, need to be investigated in proper scientific studies.
2) What can be said about the amount of carbon dioxide trapped in deep ocean layers of water as compared to its capacity to hold carbon dioxide.
3) Bodies of water can dissolve more carbon dioxide at
4) What is a the thermocline?
5) How does the thermocline act to keep carbon dioxide locked in ocean waters?