So many important reactions involve equilibria that scientists have sought to find a mathematical expression they can apply in order to provide the right conditions to best manipulate these reactions. A mathematical expression was found that gives a constant value, at the same temperature, when the system has reached equilibrium. The expression is given below and is known as the reaction quotient or equilibrium expression.
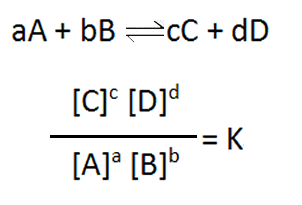
Now the reaction quotient has different values as the reaction proceeds, depending on the mixture of substances in the reaction vessel. Is is only when the system reaches equilibrium that the value of the reaction quotient remains constant at a value known as the equilibrium constant (Kc).
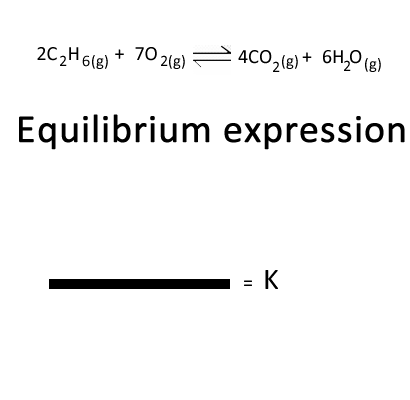
K, the reaction quotient, is equal to Kc only when the system has reached equilibrium.
Click to see the equilibrium expression for the combustion of ethane form from the equation given on the left.
The equilibrium expression is different for each equation. For example
take the same reaction as on the left but with different coefficients
in front of the reactants and products.
![]()
The equilibrium expression will
be as shown below
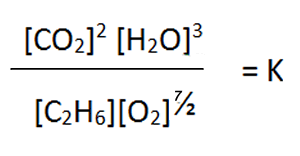
Therefore, it is important when
the value of an equilibrium constant is quoted that the equation is also
specified.
But
what does the equilibrium constant tell us about the reaction?
The higher the value of the equilibrium constant the greater the amount
of product that is formed. In other words the greater the value of Kc the greater is the extent to which the reaction moves to the right.
For values of Kc of less than 10 -4,
significant amounts of reactants are present at equilibrium and little
product is formed. While for values greater than 10 4, the
formation of product is favoured. For values of Kc in between
these, significant amounts of product and reactants remain at equilibrium.
The Kc values of three reactions are given below.
1) Kc = 2 X 10 10,
2) Kc = 0.34
3) Kc = 2 X 10 -12,
The only reaction out of the three that favours the formation of products
is 1). It has a significantly higher "Kc" value
Lets see how
we can use the mathematical expression of equilibria to calculate and
predict products and reaction conditions.