Paper chromatography
Chromatography is a technique used to separate the components of a mixture.
Paper chromatography is one of the simplest chromatographic techniques.
All the methods of chromatography involve a stationary phase and a mobile
phase. With paper chromatography the stationary phase is the paper while
the mobile phase is the solvent in which the sample is dissolved. The
many components of the sample mixture are dissolved in the solvent and
carried up the paper. The degree to which the different components of
the mixture separate depends on the strength with which each component
is attracted to the stationary phase (paper) and its solubility in the
mobile phase (solvent). In paper chromatography, the size of the component
particles is also a major factor in determining how far each component
rises.
Each component of a mixture can be identified by comparing the distance travelled along the stationary phase to the distance travelled by the mobile phase. This is expressed as an Rf value for the component. Each component of a mixture has its own Rf value for the conditions under which the technique was performed.
Consider the animation on the right. It shows a black ink mixture being separated into its components and how the Rf value is obtained. The Rf value of the red ink is measured at 0.6.
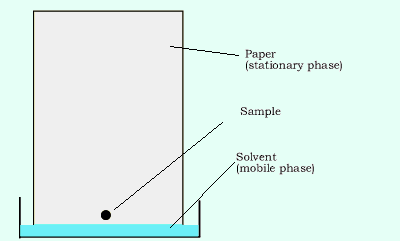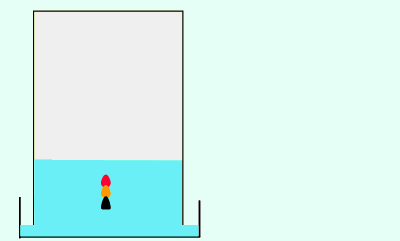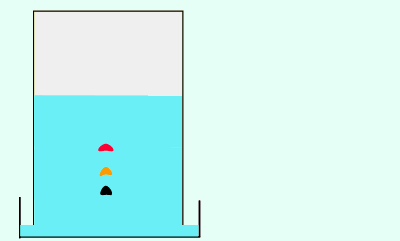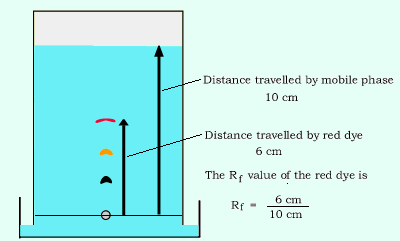
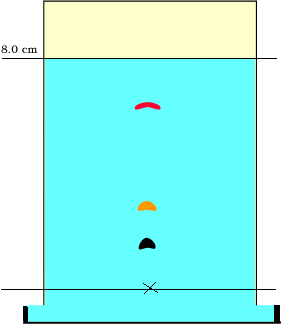
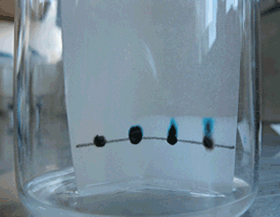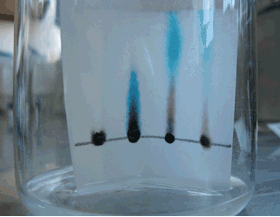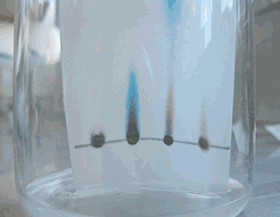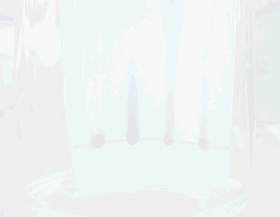
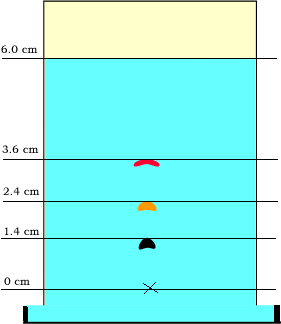
A mixture of three amino acids was separated using paper chromatography. The chromatogram is shown on the right. "X" marks the origin.
a) Explain how an Rf value is calculated.
b) Can an Rf be greater than1? Explain.
c) Calculate the Rf value of the red and yellow coloured amino acids.
d) What factors determine the different Rf values of the different amino acids?
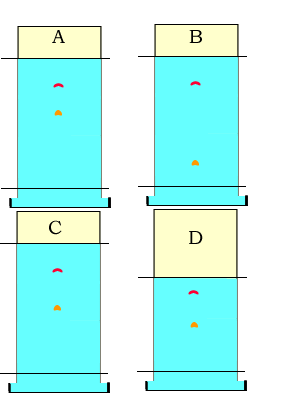
2) Consider the chromatogram on the right of an ink sample. The Rf value of the red dye component is 0.8.
What is the distance travelled by the red component if the solvent front travels 8.0 cm.