Skin
The skin is the largest organ of the body. It is a complex organ designed to perform many functions.
It forms part of the integumentary system that consists of the largest organ in the body, the skin, hair, nails, glands, and sensory nerves. . Below are some functions of the integumentary system.
-protects the body from bacteria, fungi and viruses,
-prevents dehydration,
-stores fat and produces vitamins and hormones,
- protects against harmful UV radiation,
- helps to maintain temperature.
The skin is composed of two
layers:
- an outer layer called the epidermis
- an inner layer called the dermis.
Click to see a larger view of the cross
section of the skin worksheet.
The epidermis is primarily responsible for protection of the body by providing a tough, flexible and water proof covering. The epidermis is made up of many layers of epithelial cells. These cells are specially designed to enable the epidermis in forming a complete cover.
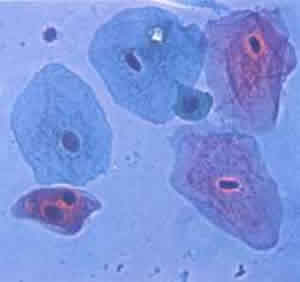
Epithelial cells are flat and overlap each other, as seen on the right. At the bottom of the epidermis is a layer of cells which is constantly dividing. This layer is the source of new cells that are constantly needed to replace old and worn out cells as they flake off the surface of the skin. The new cells grow and are pushed upwards towards the surface. As they go further up they become flatter and wider and develop a build up of a protein called keratin. As they near the surface of the skin the epithelial cells die. These dead cells provide a tough, thick, waterproof, layer that completely covers the body.
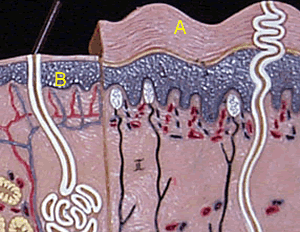
This layer of dead cells varies in thickness in different parts of the body depending on the wear and tear on that particular part. The skin on the soles of our feet, for example, is thicker than the skin on our head. The relative thickness of each area is shown on the right, where "A" represents the thickness of skin on the soles of our feet and "B" the thickness of skin on our foreheads.
Dandruff is an example of the skin continually renewing itself.
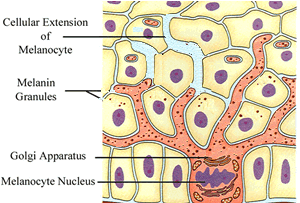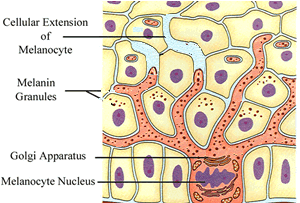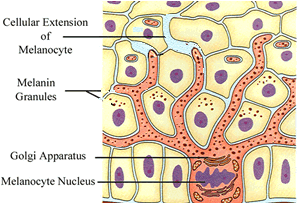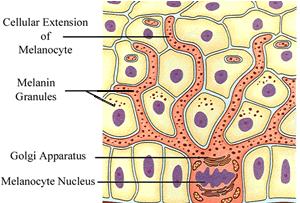
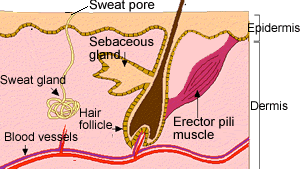
Touch receptors are found in the
During hot days the skin looks red because tiny blood vessels close to the surface of the skin dilate. These blood vessels are found in the
Dandruff is
Dandruff is
The germinal layer separates the dermis from the epidermis. This layer
The skin on the palm of one's hand is thicker than on other parts of the body. What is the best explanation for this?
Sebaceous glands produce
Many advertisements mention skin creams with vitamins that rejuvenate the skin. Why is this rejuvenation by vitamins a false claim?
What part of the skin must be targeted to stop dandruff completely? What effect would this have on the thickness of the skin?
Acne is a result of infection by bacteria of hair follicles. The best cure is washing with an
How do sebaceous glands help stop acne from developing?
Skin cancer is common amongst those that spend long hours unprotected in the sun. How does the skin guard against U.V. radiation?
Antiaging creams are big business. Some creams are said to contain elastin and collagen that rejuvenate the skin. Look at the commercial on the right. Argue against such treatments.
What are elastin and collagen?
What is their purpose in the structure of the skin?
Some people argue that the anti-wrinkle creams are nothing more than moisturising creams that help the skin absorb water. How does this remove wrinkles?
With some research, describe how the integumentary system:
- controls body temperature,
- protects vulnerable cells from harmful radiation,
- offers protection from pathogens (harmful microbes)
What Vitamin is produced by the skin? What is the role of this vitamin in the body?
