When a cell, such as the a red blood cell, pictured on the right, is immersed in an isotonic solution its volume remains constant as water moves in and out at equal rates. Both the external and internal solutions have the same concentration. A cell in this state is said to be isotonic to the surrounding solution.
A cell in a hypotonic solution, which has a lower solute concentration than the cell, will gain water and is likely to burst.
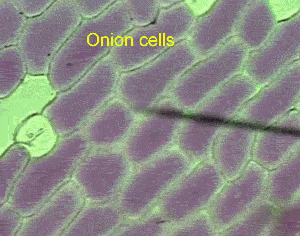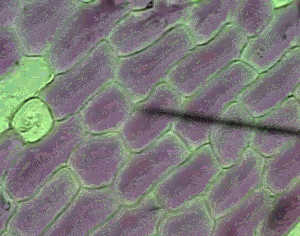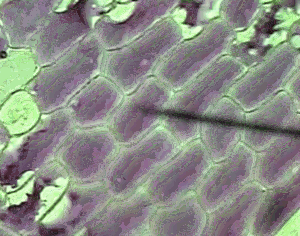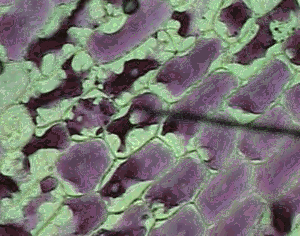
However a cell in a hypertonic solution is likely to lose water, shrivel and die from dehydration. Look at the onion cells on the right placed in a hypertonic solution.
For these reasons osmoregulation, control of water balance, is important to the survival of the organism. Animals have ways of preventing excessive water loss and dehydration.