Relationships
Living together = Symbiosis

Symbiosis means living together. It is an interaction between 2 organisms where at least one of these organisms benefits. The benefit may be in the form of :
-food,
-transport,
-protection,
-grooming,
or all of the above.

Take the green ant (Oecophylla smaragdina) for example, this aggressive ant nests in trees where it provides protection from insects that harm the tree. In return the tree provides nourishment for the ants in the form of nectar.
The picture shown on the right of a flame tree in Arnhem Land, Australia, clearly shows how green ants nest in the foliage of trees. Click to see a detailed image.

Green ants use the foliage of the plant to build nests. These nests are made by joining leaves together using a silky substance produced by their larvae.
If the leaves are not close enough to be bound, ants form ant chains to pull the leaves close together.
Click to see a more detailed image

Click to see a detailed image

There are three different types of symbiotic relationships, these include:
- commensalism
- where one organism benefits but the other is neither harmed nor does it benefit.
- parasitism - where one organism benefits while the other is harmed
- mutualism
- where both organisms benefit.
An example of mutualism is the relationship between bees and flowering plants. Both organisms benefit in the relationship, the bee derives nectar and pollen from the plant while the plant becomes cross fertilised by the bees.
On the right is a picture of an Australian native bee, known as the blue banded bee (Amegilla cingulata) Click to see a detailed image.



Another type of relationship is known as a predator-prey relationship. Simply put, a predator is an organism that eats another organism. The organism being eaten is the prey while the organism eating the other is the predator. For example, a dragonfly will eat flies and therefore the dragonfly is the predator while the fly is the prey.
This predator-prey relationship does not only apply to animals it can also apply to plants such as when a grasshopper eats grass, the grasshopper is the predator while the prey is the grass. Predator-prey relationships evolve over time, where the predator evolves all that is needed to successfully its prey. This may include camouflage, speed or bigger jaws.
Click to see a detailed image of the dragonfly

1) Acacia seeds have a small capsule of sugar on one end. Ants collect the seeds in their nests for the sugar. While in the ant's nest the seeds are safe from bushfires. This relationship evolved over thousands of years and is an example of

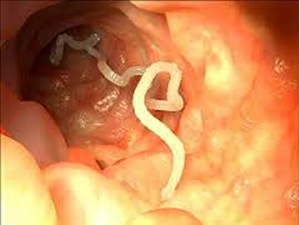





12) Organism "A" invades the body of organism "B" and lives in the red blood cells. Red blood cell count decreases significantly in organism "B" to the point where organism "B" can not function.
a) Which organism is the host?
b) What is another name for organism "A"?
c) Which term best describes the relationship between A and B? Explain.