
An ecosystem consists of three essential components.
- A living component (biotic) made of different populations of different organisms, some of which are microscopic and also the organic matter produced by these organisms such as faeces or decaying, organic matter.
- A non-living component (abiotic). Examples include, water, minerals, energy, rocks, sunlight, temperature and cloud cover.
- The interaction amongst the biotic factors and the abiotic surroundings.
Habitat is a place where a population lives. Populations can move from habitat to habitat if the conditions are not right.
What happens in an ecosystem?
As discussed above, an ecosystem involves very dynamic and self sustaining interactions between individual organisms and the non-living (abiotic) parts of the ecosystem. In every ecosystem energy must be captured and brought into the ecosystem and nutrients must be recycled.
Two sets of organisms are critical to any ecosystem, that being the producers and the decomposers. In fact the most simplest of ecosystems simply contains a population of producers and a population of decomposers as well as the vital abiotic factors, such as energy, water and nutrients.
As organisms undergo cellular respiration, energy is lost as heat. This is why energy must be constantly supplied to an ecosystem.
Heat is necessary to sustain life and the fact that it is constantly lost to the environment is evident on a cold day as water vapour condenses in the air as we breath out warm air.
Decomposers also undergo cellular respiration and release heat energy. A compost heap will produce a great deal of heat as the process of decompostion takes place.
Consider the animation on the right. It shows how food passes through a food chain.
a) What is passed from plant to the rabbit to the fox and finally to the decomposers?
b) What do the decomposers recycle?
c) At every step along the food chain
what is lost?
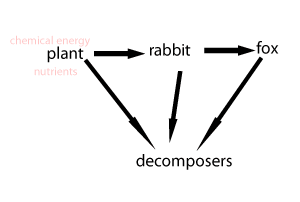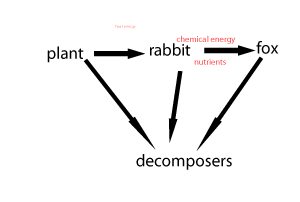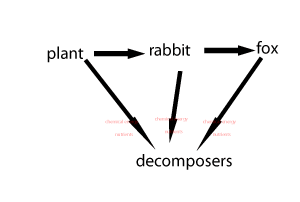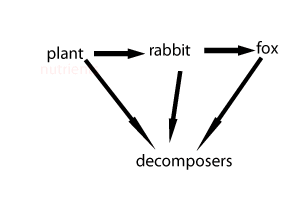
Producers are organisms that can trap an external energy source and convert it into a form that can be stored and used by other members of the ecosystem. Usually, this form of energy, is in the form of chemical energy.
Some organisms, such as algae and plants trap light energy in a process called photosynthesis.
While other organisms, in extreme environments such as deep on the ocean floor, use the energy in sulfur compounds, such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S) escaping from hydrothermal vents, to manufacture their own chemical energy. This process is known as chemosynthesis and is carried out by micro-organisms, such as bacteria, generally known as chemoautotrophs. Chemosynthesis is the conversion of two or more molecules of carbon dioxide (CO2) or methane (CH4) into organic matter using energy derived from hydrogen sulfide or methane. Chemosynthesis can sustain large ecosystems in environments that lack sunlight and oxygen.

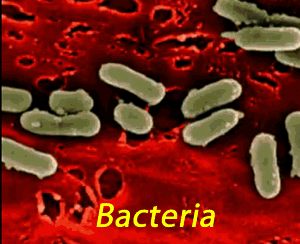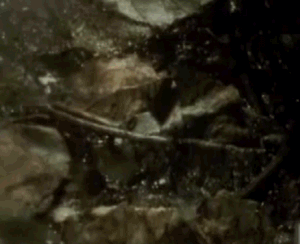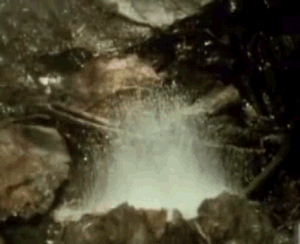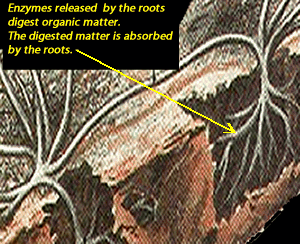
Decomposers are the nutrient recyclers of all ecosystems which chemically breakdown the organic matter back to its basic building blocks ready to be used by other organisms for growing.
This group consists of bacteria and fungi (mold, mushrooms).
So we have the producers and the decomposers in our ecosystem, but there are other groups of organisms than just these two groups.
Consider the food chain on the right. It shows a cow a wolf and a worm. All these three organisms are known as consumers. This group of organisms must obtain their food by eating other organisms or parts of them.
1) Consider the food chain on the right. The arrow points in the direction that chemical energy passes from one organism to the next.
a) What is the group that grass belongs to?
b) The loss of which two organisms would cause the ecosystem to collapse?
c) Mushrooms and molds belong to a group of organisms known as fungi. Fungi are
d) An arrow points from the wolf to the worm indicating that the worm gets chemical energy from the wolf. Does this mean the worm eats the wolf? Explain.
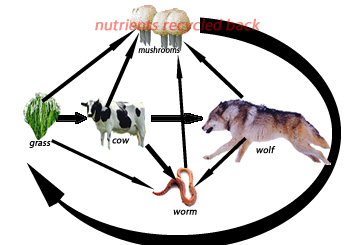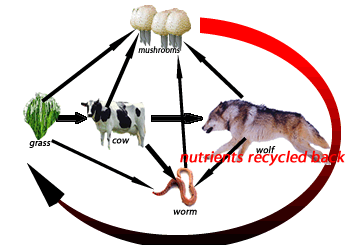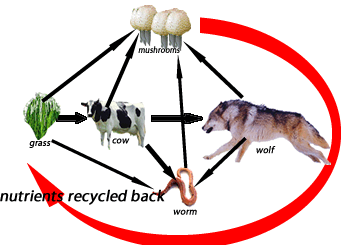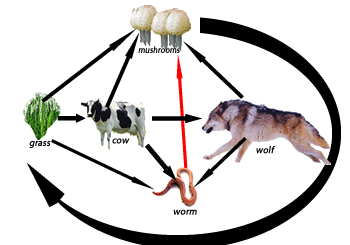
Consider the terrarium shown on the right. It represents a closed ecosystem.
2) Which of the following represent the abiotic factors of this community?
3) The energy to power this ecosystem comes from
4) Which of the following are not recycled in this ecosystem

5) The process of photosynthesis fixes into which can be stored and passed on from organism to organism.
6) Chemoautotrophs can sustain large ecosystems deep on the ocean floor where oxygen and light are absent. The energy to sustain such ecosystems comes from a process known as
7) Food is another name for
8) Which one is not a producer
9) A mushroom belongs to a group of organisms commonly referred to as
10) The two essential groups of organisms in an ecosystem are the
Continue with the Cane Toad
Continue with ecosystems and recycling